Xiaomi Forges Ahead with Tesla-Inspired SUV as Debut EV Hits Targets
Summary
Xiaomi intends to enter the electric vehicle (EV) market by 2025, commencing with SUVs, starting with the SU7 model. With a goal to diminish dependence on smartphones, the company is poised to rival competitors like Tesla and BYD, having garnered positive market feedback and forecasting potential profitability by 2026.
Xiaomi Corporation aims to commence production and sales of a sport utility vehicle akin to Tesla Inc.’s Model Y as early as 2025, marking a significant expansion with the manufacturing of its inaugural SU7 electric car expected to reach around 100,000 units this year.
Approaching maximum initial capacity, Xiaomi is presently focused on enhancing output to meet rising demand, according to individuals familiar with the matter. The company reportedly used Tesla’s SUV as a benchmark during development, these individuals disclosed on condition of anonymity due to the project's confidentiality.
Introducing an SUV would signify a substantial enlargement of Xiaomi’s $10 billion EV venture, spearheaded by billionaire co-founder Lei Jun. Seeking to lessen reliance on the volatile smartphone market dominated by Apple Inc., Xiaomi ventures into a competitive domain, challenging established rivals such as Tesla and BYD Co.
Xiaomi's exact specifications and pricing for the SUV remain undisclosed, although SUVs are gaining popularity in China. Plans for production, initially disclosed by local media outlet Yicai, may evolve based on progress in capacity expansion, the sources added. Xiaomi representatives did not respond to inquiries via email or phone.
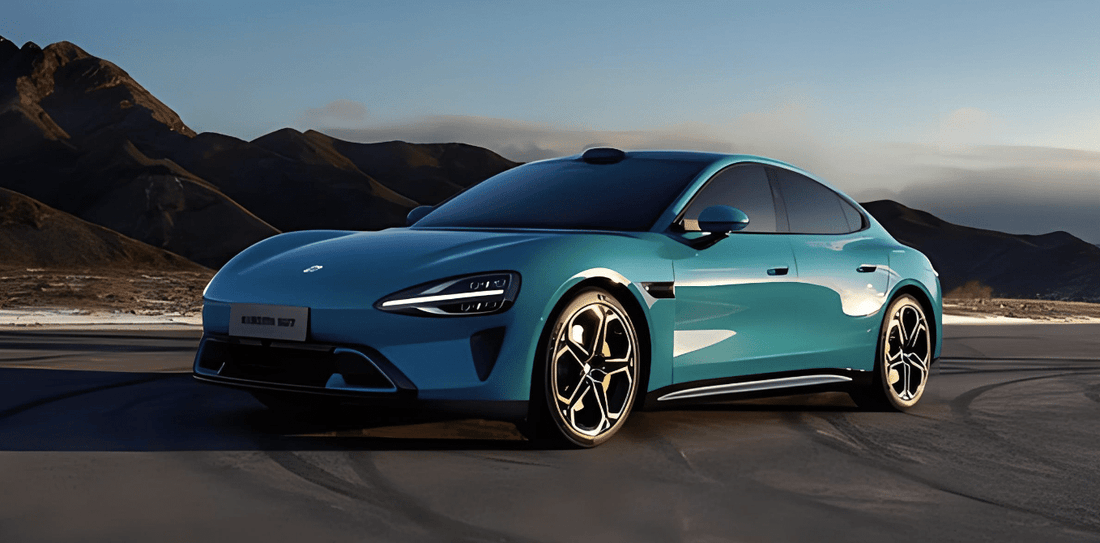
Discussions about an SUV began as early as Lei's announcement in 2021 that EVs would represent his final major entrepreneurial endeavor, according to one source. However, the company opted to prioritize the SU7, a sedan priced at $30,000 and above, featuring a design reminiscent of Tesla’s Model 3 and the Porsche Taycan.
Xiaomi anticipates that the SUV won’t enter mass production until at least late 2025, coinciding with the completion of the second phase of its assembly factory in Beijing, as per one source. Currently, the focus is on SU7 production, with capacity allowing for fewer than 10,000 deliveries per month, the source added.
With over 60% of its revenue derived from smartphones, Xiaomi has been diversifying, partly due to sluggish device demand in its home market.
Yet, it joins numerous contenders competing for a share of the Chinese EV market, the world’s largest, albeit one where margins have dwindled due to a price war led by Tesla and BYD amidst slowing growth. Apple abandoned its long-incubated EV project after grappling with challenges in applying its technological expertise to a new manufacturing sector.
Xiaomi’s SU7 series amassed nearly 90,000 confirmed orders by the end of April, approximately a month after its late March debut. Xiaomi's stock has surged approximately 30% since the SU7's launch, nearing its highest level in roughly two and a half years.
According to analysts Frank He and Steven Wang from HSBC Qianhai Securities, Xiaomi's EV business could break even in 2026 — two years earlier than previously estimated — owing to enhanced capacity and favorable market reception for premium models. They forecast shipments to more than double to 240,000 units in 2025. “The capacity bottleneck is expected to ease in the third quarter of 2024,” they stated in a recent memo.
Xiaomi intends to enter the electric vehicle (EV) market by 2025, commencing with SUVs, starting with the SU7 model. With a goal to diminish dependence on smartphones, the company is poised to rival competitors like Tesla and BYD, having garnered positive market feedback and forecasting potential profitability by 2026.
Xiaomi Corporation aims to commence production and sales of a sport utility vehicle akin to Tesla Inc.’s Model Y as early as 2025, marking a significant expansion with the manufacturing of its inaugural SU7 electric car expected to reach around 100,000 units this year.
Approaching maximum initial capacity, Xiaomi is presently focused on enhancing output to meet rising demand, according to individuals familiar with the matter. The company reportedly used Tesla’s SUV as a benchmark during development, these individuals disclosed on condition of anonymity due to the project's confidentiality.
Introducing an SUV would signify a substantial enlargement of Xiaomi’s $10 billion EV venture, spearheaded by billionaire co-founder Lei Jun. Seeking to lessen reliance on the volatile smartphone market dominated by Apple Inc., Xiaomi ventures into a competitive domain, challenging established rivals such as Tesla and BYD Co.
Xiaomi's exact specifications and pricing for the SUV remain undisclosed, although SUVs are gaining popularity in China. Plans for production, initially disclosed by local media outlet Yicai, may evolve based on progress in capacity expansion, the sources added. Xiaomi representatives did not respond to inquiries via email or phone.
Discussions about an SUV began as early as Lei's announcement in 2021 that EVs would represent his final major entrepreneurial endeavor, according to one source. However, the company opted to prioritize the SU7, a sedan priced at $30,000 and above, featuring a design reminiscent of Tesla’s Model 3 and the Porsche Taycan.
Xiaomi anticipates that the SUV won’t enter mass production until at least late 2025, coinciding with the completion of the second phase of its assembly factory in Beijing, as per one source. Currently, the focus is on SU7 production, with capacity allowing for fewer than 10,000 deliveries per month, the source added.
With over 60% of its revenue derived from smartphones, Xiaomi has been diversifying, partly due to sluggish device demand in its home market.
Yet, it joins numerous contenders competing for a share of the Chinese EV market, the world’s largest, albeit one where margins have dwindled due to a price war led by Tesla and BYD amidst slowing growth. Apple abandoned its long-incubated EV project after grappling with challenges in applying its technological expertise to a new manufacturing sector.
Xiaomi’s SU7 series amassed nearly 90,000 confirmed orders by the end of April, approximately a month after its late March debut. Xiaomi's stock has surged approximately 30% since the SU7's launch, nearing its highest level in roughly two and a half years.
According to analysts Frank He and Steven Wang from HSBC Qianhai Securities, Xiaomi's EV business could break even in 2026 — two years earlier than previously estimated — owing to enhanced capacity and favorable market reception for premium models. They forecast shipments to more than double to 240,000 units in 2025. “The capacity bottleneck is expected to ease in the third quarter of 2024,” they stated in a recent memo.















